Knee Deep: Unraveling the Causes of Knee Issues and How to Prevent Them in Dallas TX
Knee Deep: Unraveling the Causes of Knee Issues and How to Prevent Them in Dallas TX
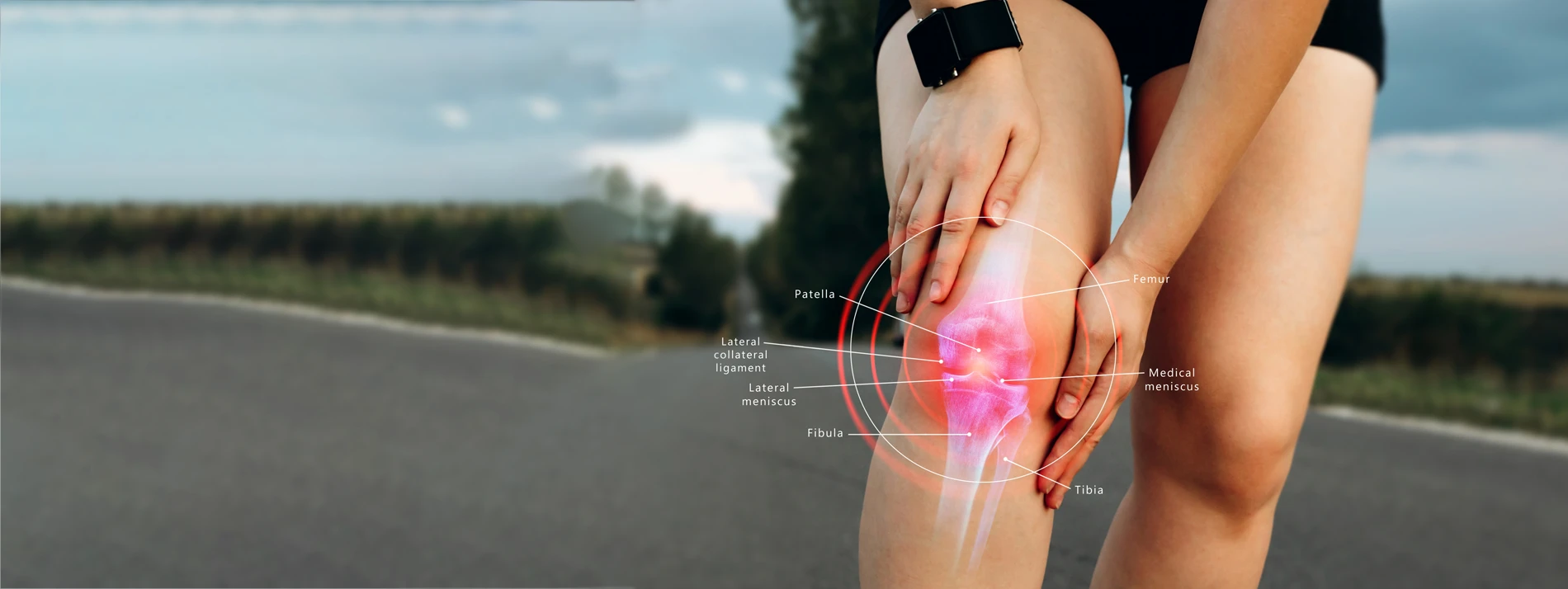
Knee issues are among the most common complaints, affecting people of all ages and lifestyles. Understanding the causes of knee problems can help you take preventive measures and seek appropriate treatments. In this blog, we'll delve into the three primary causes of knee issues: trauma, wear and tear, and tracking biomechanical issues. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how these factors contribute to knee pain and dysfunction. Contact our Dallas TX chiropractic clinic today to learn more.
Trauma: The Immediate Cause of Knee Problems in Dallas TX
Trauma refers to any sudden injury to the knee, which can result from accidents, sports activities, or falls. Traumatic injuries are often acute, leading to immediate pain, swelling, and instability.
Common Types of Knee Trauma:
- Ligament Injuries:
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Tears: Often seen in athletes, ACL tears occur due to sudden stops, changes in direction, or direct blows to the knee.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Tears: These are less common than ACL injuries and typically result from a direct impact to the front of the knee.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Injuries: Usually caused by a direct blow to the outside of the knee, common in contact sports.
- Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Injuries: Less common and typically occur due to a direct blow to the inside of the knee.
- Meniscal Tears:
- The meniscus is a C-shaped cartilage that cushions and stabilizes the knee joint. Tears can occur due to twisting motions or direct impacts.
- Fractures:
- Fractures around the knee, including the patella (kneecap), femur (thigh bone), and tibia (shin bone), can result from high-impact trauma such as car accidents or falls.
Symptoms of Traumatic Knee Injuries:
- Immediate pain and swelling
- Difficulty bearing weight
- Instability or giving way of the knee
- Limited range of motion
- Bruising and tenderness
Treatment of Traumatic Knee Injuries:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): Initial management for most acute knee injuries.
- Physical Therapy: Essential for rehabilitation and restoring function.
- Surgery: Required for severe injuries like complete ligament tears or complex fractures.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs to manage symptoms.
Preventing traumatic knee injuries involves proper training, using appropriate protective gear, and maintaining good physical conditioning.
2. Wear and Tear: The Gradual Onset of Knee Problems
Wear and tear, or degenerative changes, are common in the knee joint due to its constant use and weight-bearing function. Over time, the cartilage that cushions the knee can wear down, leading to pain and stiffness.
Common Conditions Related to Wear and Tear:
- Osteoarthritis:
- The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA), is characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone. Age, obesity, and previous injuries increase the risk of OA.
- Chondromalacia Patella:
- Also known as patellofemoral pain syndrome, this condition involves the softening and breakdown of the cartilage on the underside of the kneecap, causing pain and swelling.
Symptoms of Degenerative Knee Conditions:
- Gradual onset of pain, often worsening with activity
- Stiffness, especially after periods of inactivity
- Swelling and tenderness around the joint
- Decreased range of motion
- Crepitus (a grinding or clicking sound during movement)
Treatment of Degenerative Knee Conditions:
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Weight management and low-impact exercises to reduce stress on the knee.
- Physical Therapy:
- Strengthening exercises for the muscles around the knee to improve stability and reduce pain.
- Medications:
- Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, and sometimes corticosteroid injections to manage symptoms.
- Assistive Devices:
- Knee braces or orthotic devices to support the joint and improve alignment.
- Surgery:
- In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be necessary.
Preventing wear and tear involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active with low-impact exercises, and addressing minor knee issues before they worsen.
3. Tracking Biomechanical Issues: The Subtle Causes of Knee Problems
Biomechanical issues refer to problems with the way the knee moves and aligns during activity. These issues can stem from muscle imbalances, poor posture, or abnormal gait patterns, leading to improper tracking of the knee cap (patella) and other parts of the knee joint.
Common Biomechanical Issues:
- Patellar Tracking Disorder:
- This condition occurs when the patella doesn't move properly within the trochlear groove of the femur during knee movement, often leading to pain and instability.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS):
- ITBS is caused by the inflammation of the iliotibial band, a thick band of tissue running from the hip to the shin, due to repetitive friction over the knee joint.
- Flat Feet or Overpronation:
- Poor foot mechanics can lead to improper alignment of the knee, causing strain and pain.
- Hip and Core Weakness:
- Weak hip and core muscles can alter gait and knee alignment, increasing the risk of knee pain.
Symptoms of Biomechanical Knee Issues:
- Pain around the kneecap, often worsening with activities like running, squatting, or climbing stairs
- A feeling of the knee giving way or instability
- Pain on the outside of the knee (common in ITBS)
- Abnormal gait or posture
Treatment of Biomechanical Knee Issues:
- Physical Therapy:
- Exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee, hips, and core, and improve flexibility.
- Gait Analysis and Correction:
- Assessing and correcting abnormal walking or running patterns to reduce strain on the knee.
- Orthotic Devices:
- Custom insoles or shoe inserts to correct foot alignment and improve knee mechanics.
- Manual Therapy:
- Techniques such as massage or joint mobilization to address muscle imbalances and improve movement patterns.
- Activity Modification:
- Adjusting activities to reduce stress on the knee and allow for proper healing and alignment.
Preventing biomechanical knee issues involves regular exercise to maintain strength and flexibility, proper footwear, and attention to posture and gait mechanics.
Holistic Approach to Knee Health
Addressing knee issues effectively often requires a comprehensive approach that considers the interplay between trauma, wear and tear, and biomechanical factors. Here are some holistic strategies to maintain knee health:
- Regular Exercise: Engage in activities that strengthen the muscles around the knee, such as quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf exercises. Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, or walking to keep the joints mobile without excessive strain.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, accelerating wear and tear. A balanced diet and regular physical activity can help manage weight and reduce the risk of knee problems.
- Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive shoes can improve alignment and reduce the risk of biomechanical issues. Consider orthotic inserts if you have specific foot mechanics that affect your knees.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities and cool down afterward. Stretching can improve flexibility and reduce the risk of injuries.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to early signs of knee pain or discomfort. Rest and seek professional advice if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms.
- Professional Guidance: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers, such as chiropractors can help identify and address issues before they become severe. They can provide personalized exercises and treatments to maintain knee health.
Understanding the different causes of knee issues-trauma, wear and tear, and tracking biomechanical issues-enables you to take proactive steps in maintaining knee health. Whether it's through preventive measures, early intervention, or seeking professional treatment, addressing these factors can significantly improve your quality of life and keep your knees functioning optimally. Remember, a holistic approach that combines physical activity, proper footwear, weight management, and professional guidance is key to keeping your knees healthy and pain-free.
Monday
8:00am - 1:00pm
2:00pm - 8:00pm
Tuesday
8:00am - 8:00pm
Wednesday
8:00am - 8:00pm
Thursday
8:00am - 8:00pm
Friday
8:00am - 1:00pm
Saturday & Sunday
Closed
Texas Functional Health Centers
411 N Washington Ave Suite 7500
Dallas, TX 75246



